Cybersecurity Fundamentals
Cybersecurity involves safeguarding data, systems, and networks from cyber threats. These threats typically seek to access, disrupt, modify, or delete sensitive information or interrupt the functioning of systems and services. This page presents the basic principles and practices of cybersecurity — providing a vital guide for those entering the field or wishing to grasp the fundamental challenges and strategies related to contemporary information security.
🔐 1. Security Fundamentals
Central to cybersecurity is an essential yet impactful question:
How can we safeguard our valuable digital resources from harm?
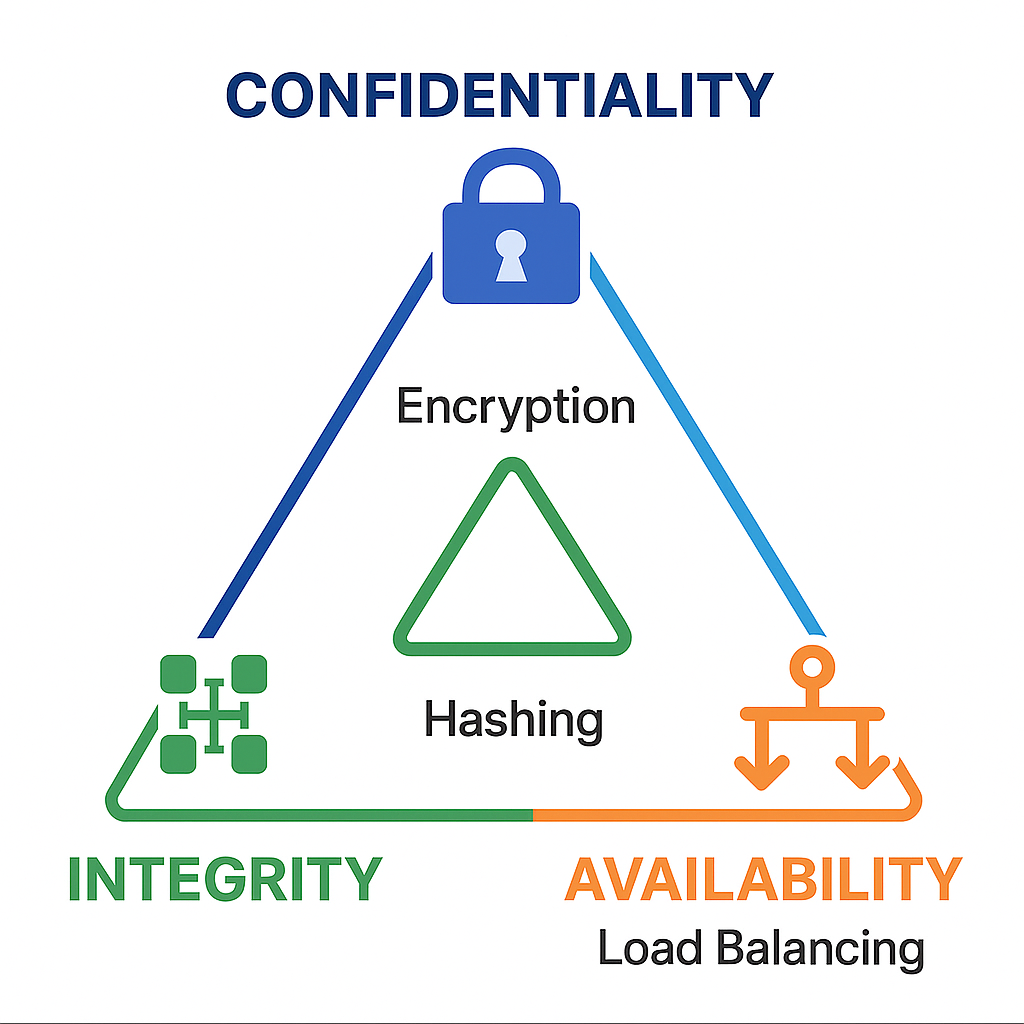
We start with the Confidentiality, Integrity, Availability (CIA Triad) — the core framework that informs almost all cybersecurity initiatives:
| Element | Description |
|---|---|
| Confidentiality | Ensuring that data is only accessible to individuals who have permission/authorisation. Techniques include encryption, access control, and data classification. |
| Integrity | Protecting data from unauthorised modification or deletion. Includes hashing, checksums, and digital signatures. |
| Availability | Ensuring that data and services are available to authorised users whenever required. This includes redundancy and disaster recovery. |
“Cybersecurity involves more than just firewalls and defence-in-depth — it requires an understanding of risk, trust, and resilience.”
Other key terms to understand include:
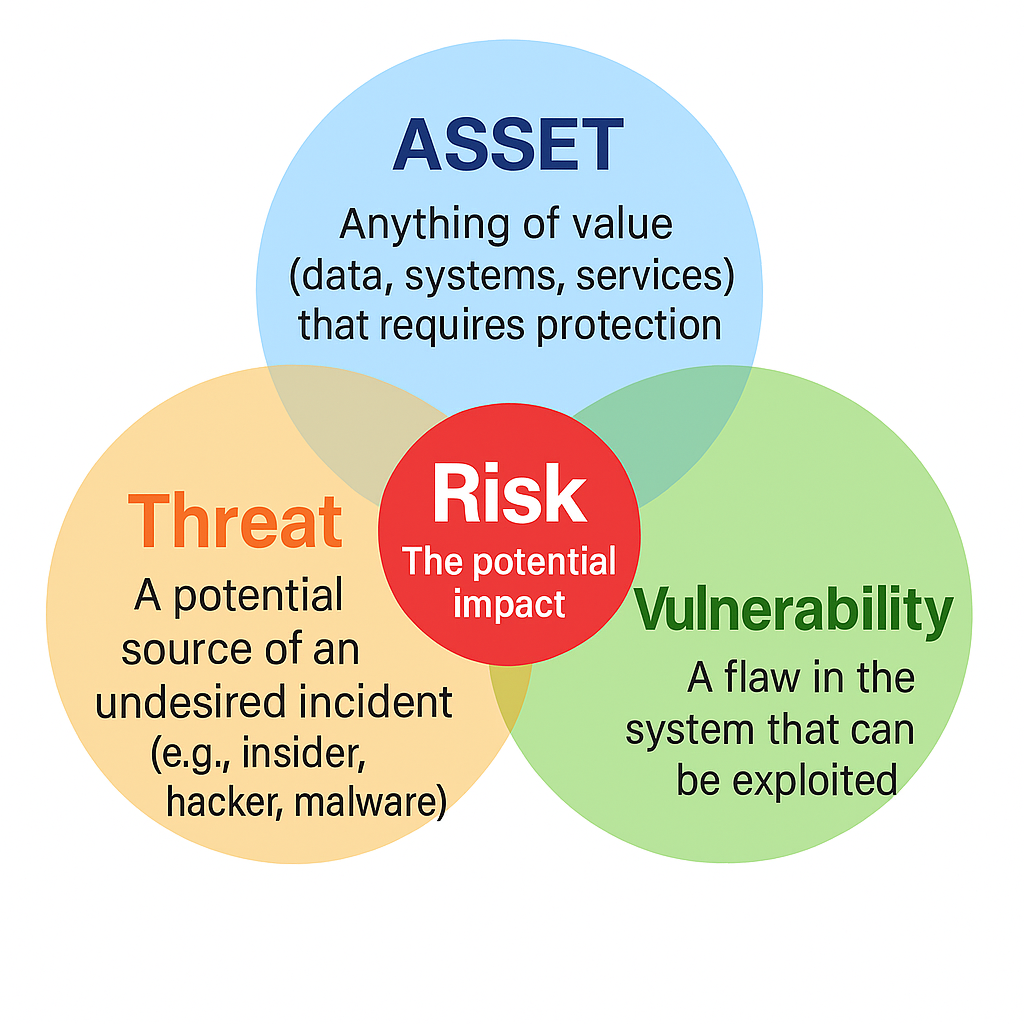
- Asset: Anything of value (data, systems, services) that requires protection.
- Threat: A potential source of an undesired incident (e.g., insider, hacker, malware).
- Vulnerability: A flaw in the system that can be exploited.
- Risk: The potential impact arising from a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
2. Elements of a Typical Cyberattack
To protect ourselves effectively, we need to understand how cyberattacks occur. Most attacks follow a phased, methodical approach — from researching targets to executing harm.
🔄 Common Stages of a Cyberattack
-
Conduct Research
Cyber attackers (or adversaries) begin with reconnaissance — gathering intelligence through public sources. This includes LinkedIn profiles, open ports, employee emails, and web applications.
They may use tools like OSINT Framework, phishing kits, and scanning platforms like Metasploit. -
Identify Targets
Once targets are identified, attackers deliver their payload — via phishing emails, malicious files, or drive-by downloads — to exploit vulnerabilities like outdated software. -
Exploit Target
The attacker breaches the system, installs backdoors, and creates persistence. Malware like ransomware or spyware is typically deployed. C2 (Command & Control) channels are established. -
Do Harmful Things
Attackers may:- Exfiltrate sensitive data (emails, credentials, business records)
- Sabotage services (erase backups, encrypt drives)
- Demand ransoms in cryptocurrencies (via ransomware)

The Cyber Kill Chain model illustrates this structured attack lifecycle.
By disrupting even one stage in the chain, defenders can often neutralize the attack altogether.
3. Elements of a Typical Security Program
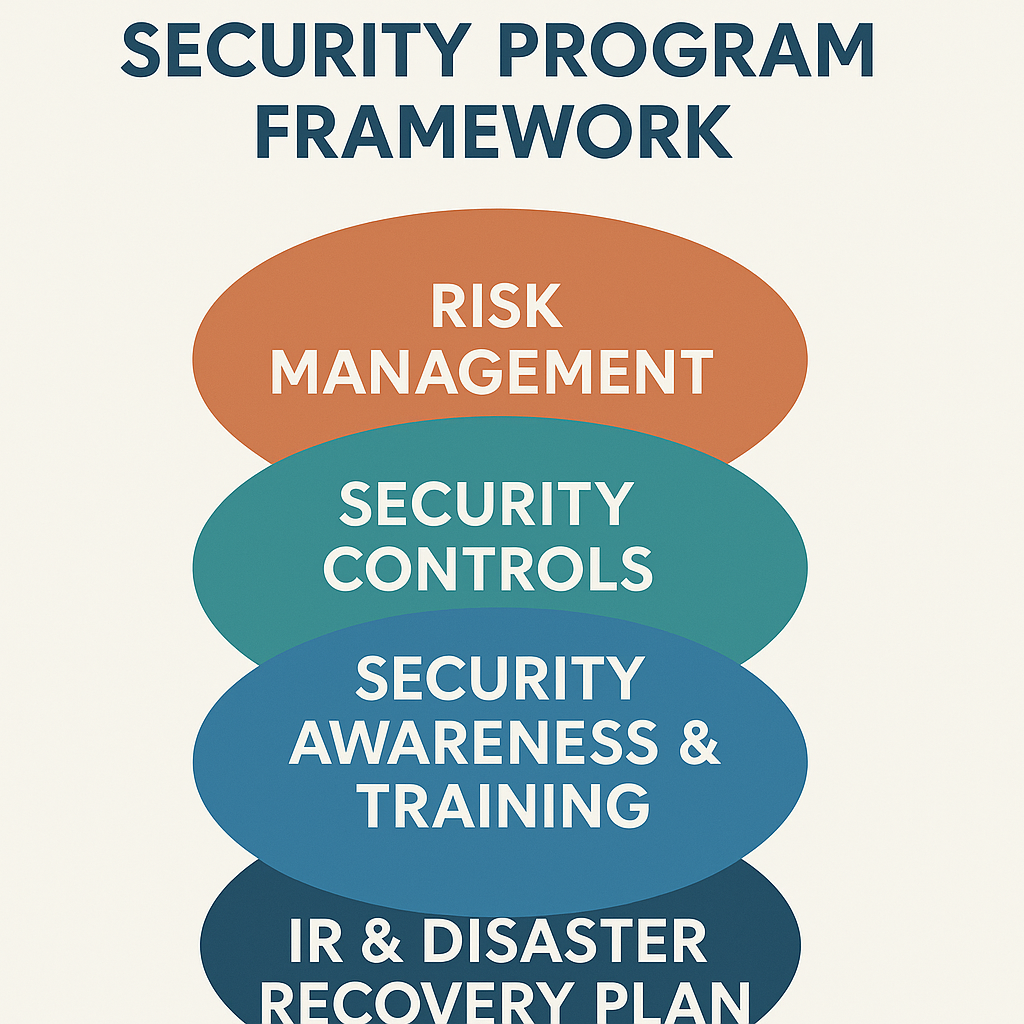
Effective cybersecurity programs include a strategic blend of governance, risk, operations, and training initiatives.
🛡️ Core Components of a Security Program
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Risk Management | Identify, assess, and mitigate potential cybersecurity risks through prioritization. |
| Governance | Establish roles, responsibilities, policies, and oversight mechanisms. |
| Security Controls | Implement technical safeguards like firewalls, endpoint protection, and access control. |
| Security Awareness & Training | Empower users to detect and respond to threats (e.g., phishing simulations). |
| Incident Response & Recovery | Establish workflows to detect, contain, investigate, and recover from attacks. |
| Ethical Responsibility | Ensure compliance with laws, responsible disclosure practices, and ethical guidelines. |
This page offers the foundational building blocks for understanding cybersecurity.
Next, explore other sections like Cyber Defense Models or SOC & SIEM to deepen your learning.